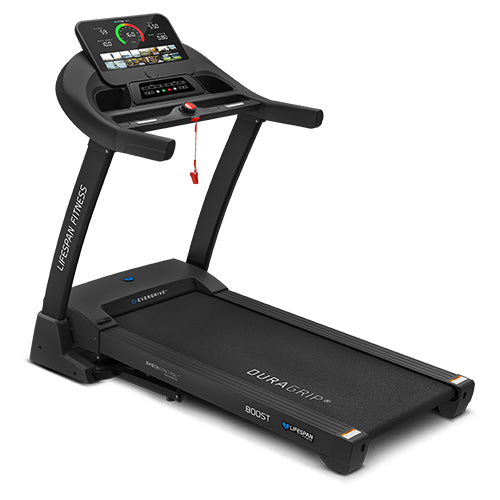
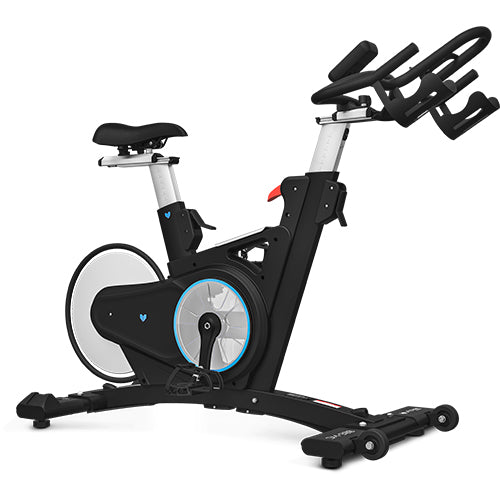
We often think of recovery as consisting of just rest and relaxation. While this is definitely an important element in any fitness routine, active recovery methods can be hugely beneficial for your muscle recovery. Light aerobic exercises, such as walking or cycling, help increase blood circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients to fatigued muscles. This promotes faster recovery by reducing lactic acid buildup and muscle soreness. While rest is important, incorporating active recovery through cardio can help your muscles heal more efficiently, allowing you to return to your fitness routine sooner. For a deeper look into why recovery is essential, visit this article on muscle recovery.
Understanding Muscle Recovery

When you exercise, particularly in strength training or intense cardio sessions, your muscles will have what are called ‘micro-tears’. Recovery is the process through which these muscles heal themselves and grow stronger. Without proper recovery, muscles can become fatigued, leading to poor performance, soreness and a higher chance of injury.
Active Recovery vs. Passive Recovery
There are two main types of recovery: active recovery and passive recovery. Both play important roles in helping your body recuperate after exercise.
- Active Recovery involves engaging in low-intensity physical activity, like walking, gentle cycling or yoga. This keeps your body moving, promoting blood flow to sore muscles, which helps clear out metabolic waste, like lactic acid, that builds up during intense workouts. Active recovery can also reduce stiffness and improve flexibility, while helping maintain a light level of physical activity without putting stress on the muscles.
- Passive Recovery is the complete rest your body takes after a workout. This form of recovery allows your muscles to fully repair without any additional exertion. While passive recovery is essential, especially after highly intense or prolonged workouts, solely relying on it can slow the recovery process. Too much inactivity can lead to stiffness or delayed muscle repair.
How Cardio Aids in Muscle Recovery
After intense workouts, your muscles accumulate lactic acid and other waste products that can cause soreness and stiffness. Low-intensity cardio, such as walking or light cycling, helps flush these byproducts from your system, speeding up the recovery process.
Engaging in light cardio post-workout also boosts the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the muscles, supporting their repair and reducing inflammation.
Cardio exercises during recovery should be kept at a moderate pace to avoid further strain. The goal is not to add stress but to gently move the body, promoting recovery while keeping muscles loose.
Best Cardio Exercises for Muscle Recovery

- Walking: One of the easiest and most accessible forms of cardio, walking helps increase blood flow to your muscles without overloading them. A 15–30-minute walk is a great post-workout activity for recovery.
- Cycling: Whether on a stationary bike or outdoors, light cycling provides a gentle, low-impact workout that engages your muscles while avoiding strain. It’s an ideal option for active recovery, especially after leg-intensive workouts.
- Swimming: Swimming is a full-body workout that allows you to move without placing weight on your joints. The buoyancy of water reduces pressure on sore muscles, while providing resistance to help maintain flexibility.
- Elliptical Machine: Using an elliptical machine engages multiple muscle groups with low impact on the joints. The smooth, repetitive movement promotes circulation and helps loosen tight muscles without overexertion.
How to Incorporate Cardio into Your Recovery Routine (200 words)
- Post-Workout Cool Down: After an intense workout, spend 5-10 minutes walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike at a slow pace. This helps lower your heart rate gradually and promotes blood flow to tired muscles.
- Active Recovery Days: Set aside one or two days per week for active recovery sessions, where you engage in light cardio activities like walking, swimming or cycling. These sessions should be much less intense than your regular workouts but will keep your body moving, aiding recovery without overtaxing your muscles.
- Low-Intensity Intervals: On strength training days, consider incorporating short, low-intensity cardio intervals, such as walking or light jogging on a treadmill between sets.
Other Tools for Muscle Recovery

- Compression Boots: Compression boots are a popular recovery tool for athletes. They work by applying controlled pressure to your legs, promoting blood flow and reducing muscle swelling. Compression therapy is particularly beneficial for recovering after intense leg workouts or endurance activities like running or cycling.
- Massage Chairs: Massage chairs provide a convenient way to relax tight muscles and ease tension throughout your body. By using targeted massage techniques, these chairs help improve blood circulation and relieve muscle stiffness. The kneading and rolling motions simulate the effects of a deep-tissue massage, making them an excellent tool for muscle recovery. Learn more about how they work in this article.
- Saunas: Heat therapy, like infrared or traditional saunas, is another effective recovery tool. Saunas help increase blood flow to sore muscles, reduce inflammation, and promote relaxation. Regular use can enhance flexibility and help prevent stiffness after intense workouts.
Conclusion
Incorporating cardio into your recovery routine can significantly enhance muscle healing by promoting blood circulation and reducing soreness. By taking a well-rounded approach to recovery, you’ll not only reduce the risk of injury but also improve your overall fitness and performance. Prioritise recovery to maximise the benefits of your exercise routine.