Introduction
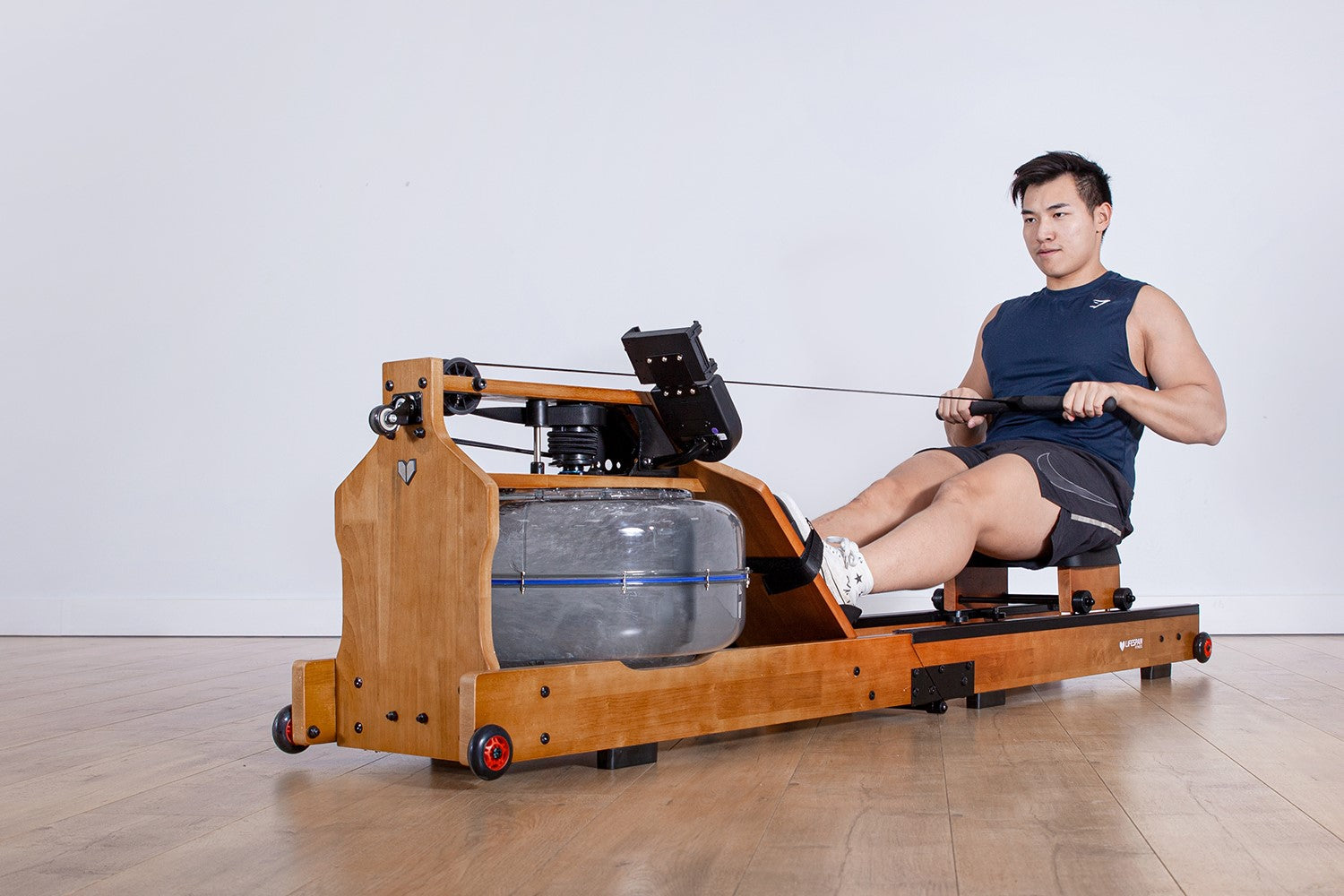
It's no secret that rowing machines are becoming one of the most popular home fitness machines. The all-encompassing workout experience facilitated by rowing machines. Renowned for their ability to deliver a complete full-body workout, rowing machines are versatile pieces of equipment capable of targeting various muscle groups simultaneously. With a variety of models to choose from, rowing machines are suitable for all ages and fitness abilities. Read on to discover the mechanics behind this efficient workout modality and uncover its potential to enhance cardiovascular health, build strength and improve overall fitness levels.
Primary Muscles Targeted

Let's delve into the intricate anatomy of rowing and dissect the major muscle groups activated during this dynamic exercise. We'll unravel the synergistic engagement of muscles and illustrate how rowing effectively targets the entire body for a comprehensive workout experience.
1. Quadriceps
The quadriceps play a crucial role in the rowing motion, serving as primary movers during the leg drive phase of the stroke. As you push against the footplates to extend your legs, the quadriceps contract forcefully, generating power to propel the rowing machine's seat backward. This action not only drives the movement of the machine but also contributes significantly to the overall intensity of the workout. Strengthening the quadriceps through rowing enhances leg strength and endurance, enabling you to sustain longer, more powerful strokes and maximising the effectiveness of your rowing session.
2. Hamstrings

The hamstrings play a crucial role in rowing exercises, particularly during the recovery phase of the stroke. As you glide forward on the rowing machine's seat, the hamstrings lengthen to allow for smooth movement, acting as stabilisers to control the deceleration of the body. Then, during the drive phase, the hamstrings assist the quadriceps in extending the legs, providing additional power to the stroke. Strengthening the hamstrings through rowing not only improves leg strength and power but also helps maintain proper form and prevent injury by balancing the forces acting on the knee joint.
3. Glutes
Rowing is an excellent exercise for activating and strengthening the glute muscles. During the drive phase of the rowing stroke, as you extend your legs against resistance, the gluteus maximus, the largest muscle in the buttocks, contracts forcefully to generate power and propel the body backward.
The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus, located on the sides of the hips, engage to stabilise the pelvis and maintain proper alignment throughout the movement. By incorporating rowing into your fitness routine, you can effectively target and strengthen these important muscles, improving overall lower body strength, power and stability.
4. Back Muscles

Rowing exerts a significant impact on the back muscles, particularly targeting the lats and rhomboids. During the rowing motion, as you pull the handle towards your torso, the lats contract to initiate the movement and continue to engage throughout the stroke to facilitate shoulder extension and adduction. Simultaneously, the rhomboids, situated between the shoulder blades, work to stabilise the scapulae, ensuring proper shoulder mechanics and posture. Strengthening these back muscles through rowing not only enhances upper body strength but also promotes better posture, shoulder stability and overall back health.
5. Core Muscles
Rowing engages the core muscles extensively to maintain stability and balance throughout the exercise. As you perform the rowing stroke, the core muscles, including the rectus abdominis, obliques and transverse abdominis, work to stabilise the spine and pelvis, preventing excessive movement and ensuring efficient transfer of force from the lower body to the upper body and vice versa. They also help to maintain proper posture and alignment, reducing the risk of injury and optimising the effectiveness of each stroke. Strengthening the core through rowing not only improves overall stability and balance but also enhances athletic performance in various other activities.
6. Arms and Shoulders
The arms and shoulders play a crucial role in the rowing movement, contributing to the overall power and efficiency of each stroke. As you pull the handle towards your body during the rowing stroke, the muscles of the arms, including the biceps, contract to flex the elbows, pulling the handle towards the chest. Simultaneously, the muscles of the shoulders, including the deltoids and rotator cuff muscles, engage to stabilise the shoulder joints and facilitate shoulder extension. By effectively coordinating the movement of the arms and shoulders, rowing maximises upper body strength and muscular endurance, promoting a balanced and efficient workout experience.
Conclusion

Incorporating rowing into your fitness routine offers an impressive range of benefits, thanks to its comprehensive muscle engagement. Rowing targets major muscle groups including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, back muscles, core muscles and arms and shoulders. This full-body workout not only improves strength and endurance but also enhances cardiovascular health, promotes better posture, and increases overall stability and balance. No matter what kind of rowing machine you're using, you'll be able to build muscle, burn calories and improve your overall fitness level. Embrace the versatility of rowing machines and unlock the transformative power of this dynamic exercise modality.
And if you have questions at all about rowing machines or need help finding the right one for you, just reach out to our team and we'll be happy to help you out.